Crypto, short for cryptocurrency, is a digital currency, used as a form of exchange.
It is secured by cryptography which makes it extremely difficult to counterfeit or hack.
Cryptography is a method of encryption allowing data to be exchanged between sender and receiver in a secure manner.
Countries around the world have their currencies. Each country has created notes and coins which have a value associated with them.
For example, that blue coloured note in your wallet, which has Dame Mary Gilmore and AB ‘Banjo’ Paterson on it, we know as $10.
The currency is not backed by anything intrinsic – so its value is whatever the government tells you it is.

So, what is crypto?
Crypto is very much the same thing – instead of notes and coins, it is code that has a value associated with it. Basically limited entries in a database no one can change without fulfilling specific conditions.
To understand crypto, let’s first understand money.
For money to be, money, it needs to satisfy the following properties:

Before the release of notes, bills and coins, people would trade.
A chicken for a blanket, a bunch of flowers for a piece of bread. Then, people would use gold or other rare resources. Carrying around a trunk of gold is not good for one’s back, so notes and coins were rolled out. Later, credit and debit cards.
Different things have been launched to do the same thing; allow you to buy and sell. Crypto is no different. A chicken, gold, a coin, a card and now, a piece of digital code.
Money as we know it (and have known it for some time) holds specific values because a Government says it does.
This is where crypto is different, as an entity doesn’t control it. Institutions and governments no longer control the worth and value.
We dictate its worth. A whole different power game has come to play.
The first cryptocurrency was Bitcoin. Satoshi Nakamoto, the unknown inventor of Bitcoin, actually never intended to invent a currency. His goal was to create a new electronic cash system that uses a peer-to-peer network to prevent double-spending.
Through this, Satoshi found a way to build a decentralised digital cash system.
The 1,600 cryptocurrencies now available emerged as a side product of Bitcoin.

Why should people trust crypto over traditional money?
Because it allows money to be decentralised.
Decentralisation occurs by way of a distributed ledger that records the crypto transactions and is held on a digital blockchain. This blockchain is then distributed and replicated over the network to allow a viable record to be kept of transactions and ownership.
Crypto decentralises money. It moves it out of the control of governments and institutions and into the hands of computers.
This can (potentially) solve things like corruption, as it moves the power from one group of people and spreads it among many.
Another concern is quantitative easing; when governments simply print more money (usually to get themselves out of debt). This can then drive down the value of their currency (if there is a whole lot more money, the value goes down and things become more expensive).
Crypto will resolve this as you can’t simply just ‘print more of it’. Governments no longer control it, nor is it printed. It is code, generated by computers.
Crypto cuts out the middleman. Now, when you want to buy with a credit card, take money out of an ATM, hold your money in a bank or transfer your money to another country’s currency, there is a small amount being taken away to pay the middleman (the bank, the ATM fee, the transfer fee, the exchange rate etc). With crypto, there is no middleman.
Most importantly, crypto has the power to put people in control of their money.
In some countries, if you don’t have a will and pass away, some governments legally, have the right to take your assets. With crypto, only you can access, move and control your assets.
How are coins made and what is blockchain?
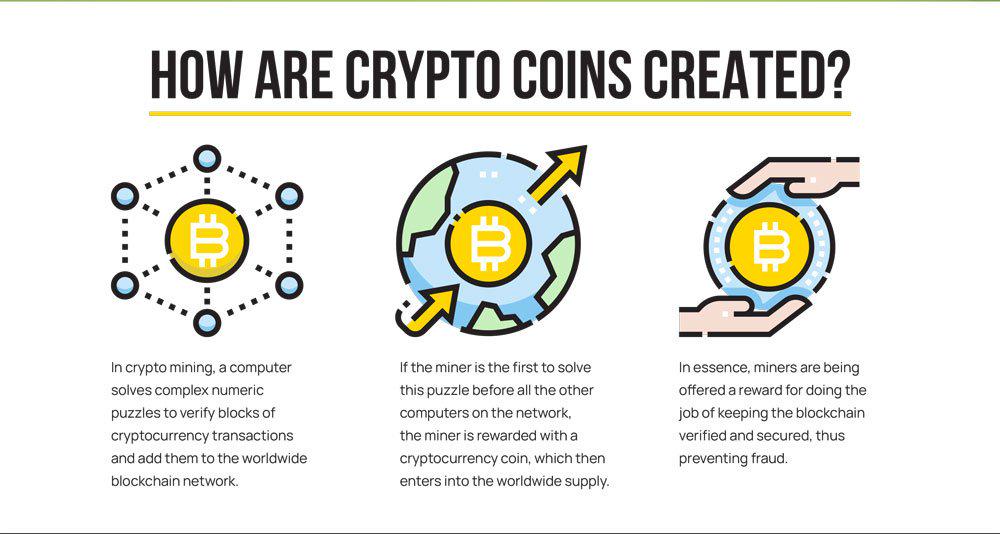
A blockchain is simply a shared database. A database is a set of data that is held in a computer and accessible in different ways.
A blockchain works by recording transactions within that block – each new link in the chain records any new transactions creating an unbroken record of who the buyer and seller were at that time. The records which make up the blockchain are immutable, meaning they cannot be changed, they can only be added to by creating more links recording transaction data. All this information is public and can be viewed by anyone with access to the internet with the correct software.
Blockchains are managed by a global network of computers. These computers are often referred to as miners.
These computers from all over the world work together to verify and transmit different entries
When you buy, sell or trade crypto, you are adding data to the blockchain.
Every user interaction is recorded (as digital code) on the blockchain. Blockchain doesn’t only record and store these movements, they also verify them. This process is a smart contract.
Smart contracts are agreements or rules, which are coded in the blockchain. This allows the blockchain to have a ‘history’ of all movements and engagements across all crypto transactions. These rules fall under the oracle, which is the source of knowledge. For example, “If it rains in 2 hours for more than 3 hours, give user Tom $5,000”.
The important thing to note with blockchain, smart contracts and Oracle, is that no single entity makes the rules or determines movements. The code is the law and because of this, cryptocurrency is exempt from corruption.
How does a piece of code equal value?
In the same way money and commodities gain value. From people.
Think of this, the value of a Chanel Boy Bag is over $8,000. When it was first made, it wasn’t. It grew in value based on the equity of the brand, the demand and the people wanting it.
Cryptocurrency gains value because people drive this up by demand. If demand increases faster than supply, the price goes up.
The supply mechanism of a cryptocurrency is always known; each crypto project publishes its token minting and burning plans.
Demand can increase as a project gains awareness or as utility increases. Broader adoption of crypto as an investment also increases demand while effectively limiting the circulating supply.
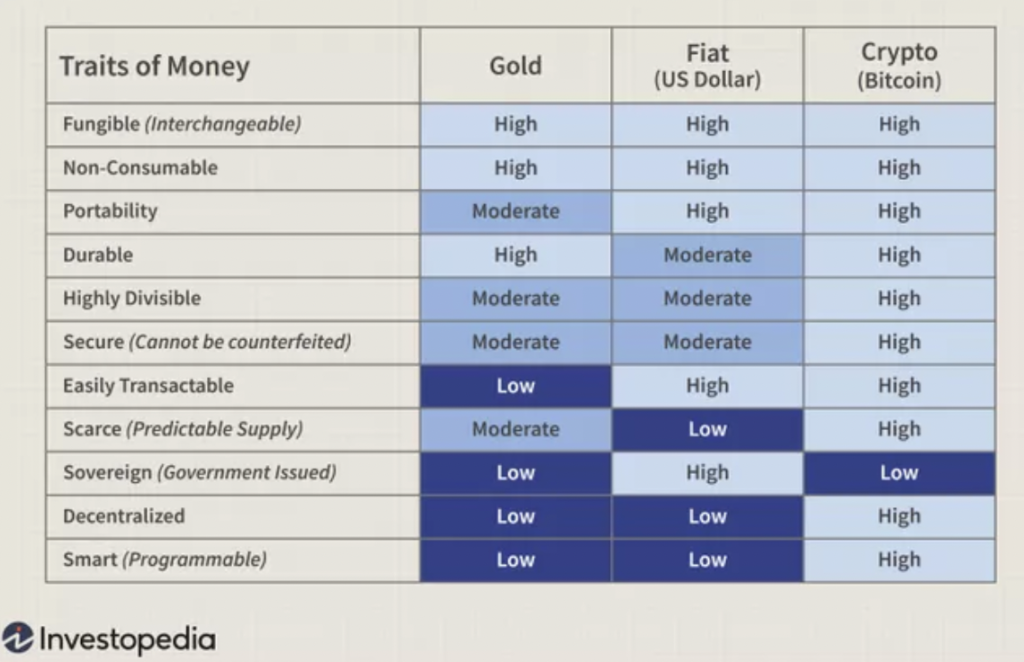
Traditional finance has been dictated and leveraged by a specific group of people. Cryptocurrency invites everyone to take part, ensuring that not only one group of people benefit by providing everyone with an equal opportunity to gain from it.





